The pulsed dye laser (PDL) is a type of laser commonly used in dermatology for various skin conditions.
Here are some key points about the pulse dye laser:
Applications: Vascular Lesions: PDL is primarily used to treat vascular lesions, including port-wine stains, hemangiomas, spider veins, and other blood vessel-related skin concerns.
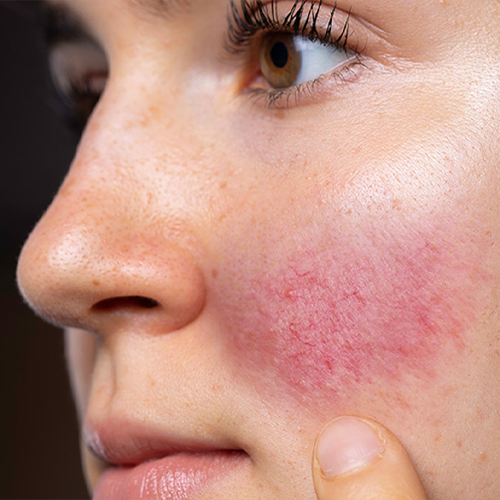
Rosacea: It may be used to reduce the redness associated with rosacea.
Scars: PDL can sometimes be used to improve the appearance of certain types of scars, especially those with a vascular component.
How It Works:
PDL emits a concentrated beam of light that specifically targets blood vessels and hemoglobin (the red pigment in blood). The hemoglobin absorbs the laser energy, causing the blood vessels to coagulate and be gradually reabsorbed by the body.
The laser’s wavelength is selected to match the colour of the target blood vessels, allowing for selective targeting without affecting the surrounding skin.
Port-Wine Stains:
PDL is particularly effective in treating port-wine stains, which are reddish-purple birthmarks caused by abnormal blood vessels near the surface of the skin. Multiple treatment sessions may be required for optimal results.
Treatment Sessions:
The number of sessions required depends on the specific condition being treated, the size of the area, and individual response to the treatment. Multiple sessions are often needed to achieve the desired outcome.
Side Effects:
PDL treatments are generally considered safe, but some temporary side effects may occur. These can include redness, swelling, bruising, or temporary darkening of the treated area. These effects usually subside over time.
Consultation with a Dermatologist:
Before undergoing PDL treatment, it is important to have a consultation with a dermatologist. They will assess your specific skin condition, discuss your medical history, and determine whether PDL is a suitable and effective option for you.
Post-Treatment Care:
Following PDL treatment, it’s essential to follow any post-treatment care instructions provided by your dermatologist. This may include avoiding sun exposure, using sunscreen, and moisturizing the treated area.

ABOUT
Dr.Aiza
Dr Aiza Jamil is a one of the leading UK trained Consultant Dermatologist, laser and aesthetics. Dr Aiza Jamil did her dermatology training in Sheffield and works as Consultant Dermatologist in Manchester University Hospitals providing services to UK’s largest hospital, Manchester Royal Infirmary. She has also completed American Board Diplomate Certification in medical and cosmetic lasers from American Board of Laser Surgery making her unique in having both UK and USA qualifications.
Frequently Asked Question
Does Rosacea Affect Blood Vessels?
Rosacea (roe-ZAY-she-uh) is one of the most common skin conditions that can cause flushing or long-term redness of your face. It can also cause a boost in blood vessels and small pus-filled bumps.
Can Rosacea Cause Skin Lesions?
Redness on the face can result in pus-filled pimples and bumps that look like acne. Blood vessels visible. They typically appear as thin red lines on the nose and cheeks.
What Organs Does Rosacea Affect?
Rosacea is a chronic (chronic) skin condition which affects the face, mainly the forehead, nose, cheeks and chin. The symptoms and signs of rosacea differ and can come and go or alter as time passes.
Does Vascular Rosacea Go Away?
There’s no cure for rosacea. However, treatments may help manage the bumps, redness, and other signs. The doctor may recommend various kinds of drugs to combat it. Topical applications of medicines on your face can fight inflammation and acne or eliminate bacteria.
What Is The Most Significant Reason For The Rosacea?
The most frequently reported triggers implicated in rosacea include alcohol, spicy food, cinnamaldehyde-containing foods (e.g., tomatoes, citrus fruits, chocolate), hot drinks, and histamine-rich foods (e.g., aged cheese, wine, processed meats).
How Can You Take Care Of Rosacea Overnight?
Try Prescription Topical Medications for Rosacea
A cream for antibiotics, such as metronidazole, may reduce skin inflammation. Azelaic acid solutions also benefit by reducing inflammation and decreasing the appearance of pustules arising from rosacea. Topical oxymetazoline or brimonidine can reduce blood vessel size and decrease flushing.


